A Gentle Introduction
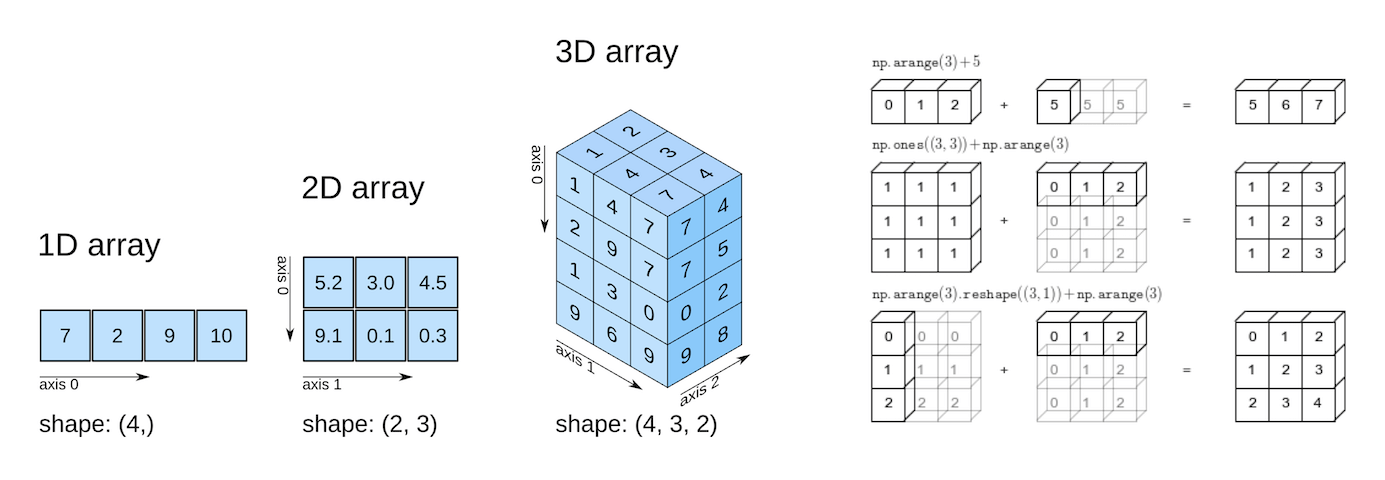 An Array is a collection of data just like lists,dictionary,sets and tuples; numpy provides more features and operation on arrays which is widely helpful in feild of data science and analytics. Its also called as a Vector and single element/constants are generally know as scalars in numpy. Array in numpy are in types: 1D array and MultiDimensional array.Generally most people use 2D and 3D arrays in Multidimensional array.
An Array is a collection of data just like lists,dictionary,sets and tuples; numpy provides more features and operation on arrays which is widely helpful in feild of data science and analytics. Its also called as a Vector and single element/constants are generally know as scalars in numpy. Array in numpy are in types: 1D array and MultiDimensional array.Generally most people use 2D and 3D arrays in Multidimensional array.
There are many array operations in numpy arrays, they are categorised into 3 types:-
1. Array with Array
2. Array with Scalars
3. Universal Array Functions
There are typically 5 basic arithmetic operations in the first 2 categories mentioned above. They are Addition, Subtraction, Multiplication, Division and Remainder operations.
Note: This article only covers from (Array with Array) operations to (Array with scalar) operations, Universal Array Function will be discussed in upcoming article 'Universal Array Function'.
Prerequisites:
Just knowledge of basic python programming and concepts of array should be known before learning this concept.
SOFTWARES REQUIRED: A pc with python and numpy installed and any IDE like vscode, pycharm or jupyter notebook is required.
Lets take an example with arr1 and arr2 with values [0,1,2] and [1,2,3] and perform the operations.
Note: Arithmetic operations in arrays can be done on operands with similar shape/size or scalars. A way to overcome this issue is Broadcasting
Addition (operator: '+')
With Array and Array:
Similar to matric addition, this operation follows result[i]=arr1[i]+arr2[i] principle.The other operation follows same principle but with their respective operators ( - , / , % , * )import numpy as np arr1= np.array([0,1,2]) arr2= np.array([1,2,3]) print(arr1+arr2)Output: [1 3 5]
return value of arr1+arr2: array([1, 3, 5])With Scalars:
The shape of scalars are represented as (1,1) and arr1 is represented as (1,3) in 2D vector representation.
Addition is done in a such a way that scalar is added to every element in array, this is followed as same in all other arithmetic operations in scalar-array operations.import numpy as np arr1= np.array([0,1,2]) # scalar '1' will be added to every element in arr1 print(arr1+1)Output: [1 2 3]
return value of arr1+1: array([1, 2, 3])
Subtraction (operator: '-')
With Array and Array:
import numpy as np arr1= np.array([0,1,2]) arr2= np.array([1,2,3]) print(arr1-arr2)Output: [-1 -1 -1]
return value of arr1-arr2: array([-1, -1, -1])With Scalars:
import numpy as np arr1= np.array([0,1,2]) # scalar '1' will be subtracted from every element in arr1 print(arr1-1)Output: [-1 0 1]
return value of arr1-1: array([-1, 0, 1])
Multiplication (operator: '*')
With Array and Array:
import numpy as np arr1= np.array([0,1,2]) arr2= np.array([1,2,3]) print(arr1*arr2)Output: [0 2 6]
return value of arr1*arr2: array([0, 2, 6])With Scalars:
import numpy as np arr1= np.array([0,1,2]) print(arr1*2)Output: [0 2 4]
return value of arr1*2: array([0, 2, 4])
Division (operator: '/')
With Array and Array:
import numpy as np arr1= np.array([2,2,1]) arr2= np.array([1,2,2]) print(arr1/arr2)Output: [2. 1. 0.5]
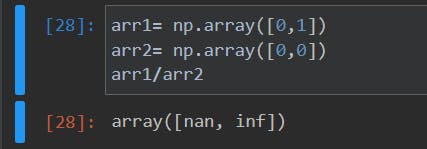
return value of arr1/arr2: array([2.0, 1.0, 0.5])- Note: There are 2 exceptional cases in division operation where python throws an error but numpy doesnt, usually in numpy 0/0 returns 'nun' and any number with divident 0 i.e; number/0 returns 'inf' (infinity)*
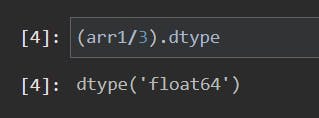
- IMP: To be noted that division operator returns resulting values in float64 datatype*
- Note: There are 2 exceptional cases in division operation where python throws an error but numpy doesnt, usually in numpy 0/0 returns 'nun' and any number with divident 0 i.e; number/0 returns 'inf' (infinity)*
- With Scalars:
import numpy as np arr= np.array([2,3,4]) print(arr/2)Output: [1. 1.5 2.]
return value of arr1/2: array([1.0, 1.5, 2.0])
Remainder (operator: '%')
With Array and Array:
import numpy as np arr1= np.array([4,5,9]) arr2= np.array([2,2,3]) print(arr1%arr2)Output: [0 1 0]
return value of arr1%arr2: array([0, 1, 0])With Scalars:
import numpy as np arr1= np.array([100,125,139]) print(arr1%10)Output: [0 5 9]
return value of arr1%10: array([0, 5, 9])
Special operation:
Exponential operation (operator: '**')
Syntax:
base_array**exponent_array
With Array and Array:
import numpy as np arr1= np.array([1,2,3]) arr2= np.array([1,2,3]) print(arr1**arr2)Output: [1 4 27]
return value of arr1** arr2: array([1, 4, 27])With Scalars:
import numpy as np arr1= np.array([1,2,3]) print(arr1**2)Output: [1 4 9]
return value of arr1** 2: array([1, 4, 9])
Conclusion:
There are still more operations on arrays and it will be discussed in my upcomming blog articles, stay tuned....
Well thank you very much for your time 👩💻
Bye ~(=^‥^)ノ👋
FOLLOW Me: likhith usurupati
LinkedIn: @Likhith

